13 Root Phenotyping Scanner – PHENOScan
Image gallery:
Contact:
Vienna BioCenter Core Facilities GmbH (VBCF)
Plant Sciences Facility (PlantS)
Dr. Bohr Gasse 3
1030 Vienna
Austria
Email: jakub.jez@vbcf.ac.at
Phone: +43664808477090
Web: https://www.viennabiocenter.org/vbcf/plant-sciences/
Key facts:
Description:
| Name | PHENOScan |
|---|---|
| Location | Vienna BioCenter (VBC), Vienna. |
| Category | Bench instrument, medium-throughput, manual sample loading |
| Environment | No |
| Sensors | Flatbed scanner |
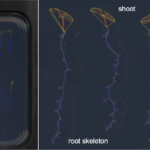
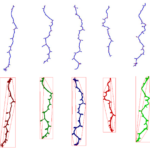
| Traits | Morphometrical root traits: Length of skeleton and individual bones; length of lateral roots; count of branching points/crossings, total root depth & width; count of individual bones and end-bones |
| Capacity | 16x agar-plates (16cmx16cm) = ~ 192 samples/seeds |
| Limitations | |
| References | |
| URL | https://www.viennabiocenter.org/vbcf/plant-sciences/phenoscan/ |
PHENOScan is a comprehensive and scalable pipeline that allows for the efficient phenotyping of root growth traits on a large scale. This includes a high-resolution, low-cost acquisition setup as well as the automated image processing software BRAT. We assess the performance of this pipeline in Arabidopsis thaliana under multiple growth conditions and show its utility by performing genome-wide association studies on 16 root growth traits quantified by BRAT each day during a 5-d time-course experiment. The most significantly associated genome region for root growth rate is a locus encoding a calcium sensing receptor. We find that loss of function and overexpression of this gene can significantly alter root growth in a growth condition dependent manner and that the minor natural allele of the Calcium Sensor Receptor locus is highly significantly enriched in populations in coastal areas, demonstrating the power of our approach to identify regulators of root growth that might have adaptive relevance.